Table layout tags
- Use the HTML
<table>element to define a table - Use the HTML
<tr>element to define a table row - Use the HTML
<td>element to define a table data - Use the HTML
<th>element to define a table heading - Use the HTML
<caption>element to define a table caption - Use the CSS
borderproperty to define a border - Use the CSS
border-collapseproperty to collapse cell borders - Use the CSS
paddingproperty to add padding to cells - Use the CSS
text-alignproperty to align cell text - Use the CSS
border-spacingproperty to set the spacing between cells - Use the
colspanattribute to make a cell span many columns - Use the
rowspanattribute to make a cell span many rows - Use the
idattribute to uniquely define one table
1 | /* Keyword values */ |
Table attributes
- align
- bgcolor
- border
- cellpadding
- cellspacing
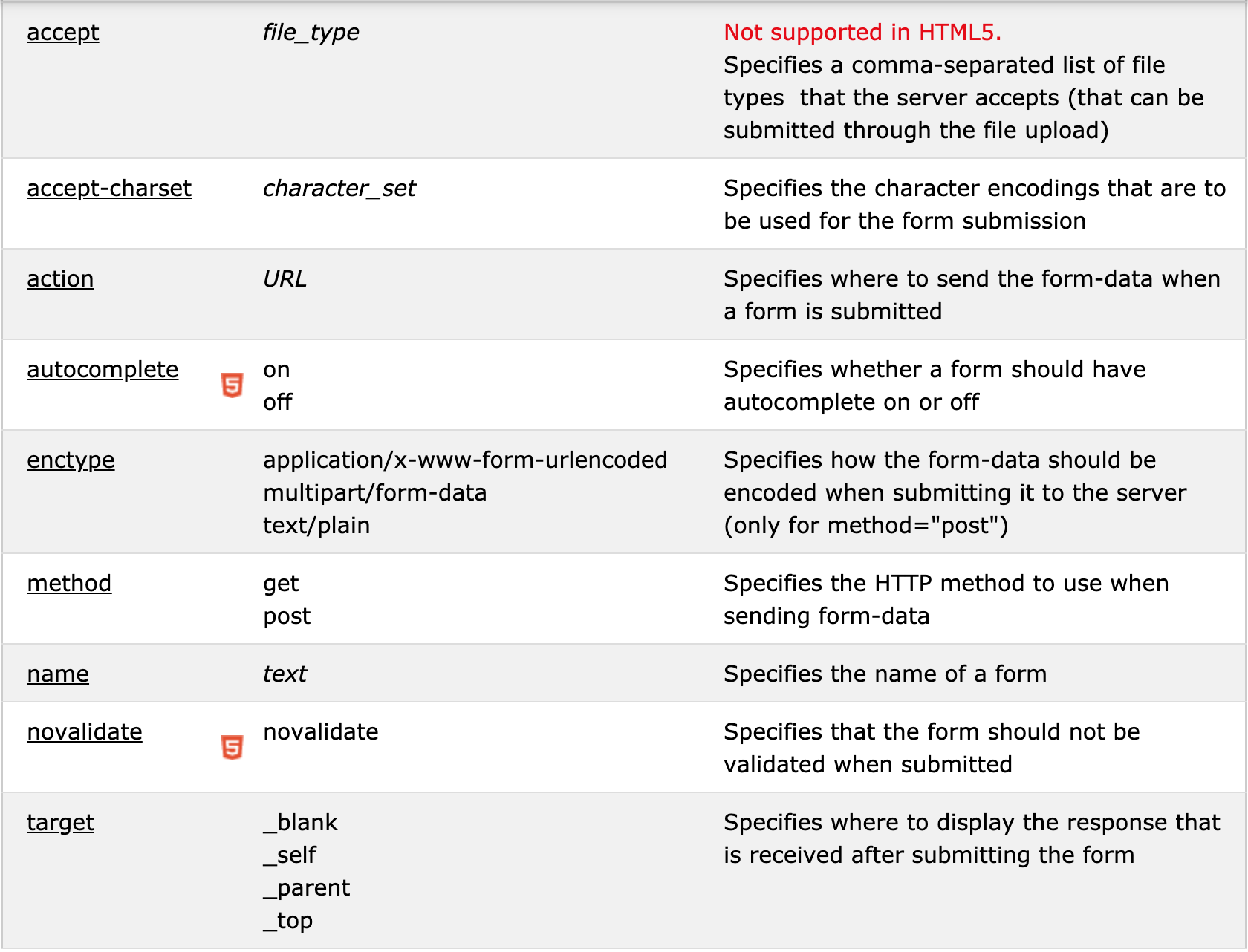
Form tags and attributes
The <form> tag is used to create an HTML form for user input.
The <form> element can contain one or more of the following form elements:
<input><textarea><button><select><option><optgroup><fieldset><label><output>
Input types
The available types are as follows:
- button: A push button with no default behavior.
- checkbox: A check box allowing single values to be selected/deselected.
- color: HTML5 A control for specifying a color. A color picker’s UI has no required features other than accepting simple colors as text (more info).
- date: HTML5 A control for entering a date (year, month, and day, with no time).
- datetime-local: HTML5 A control for entering a date and time, with no time zone.
- email: HTML5 A field for editing an e-mail address.
- file: A control that lets the user select a file. Use the accept attribute to define the types of files that the control can select.
- hidden: A control that is not displayed but whose value is submitted to the server.
- image: A graphical submit button. You must use the src attribute to define the source of the image and the alt attribute to define alternative text. You can use the height and width attributes to define the size of the image in pixels.
- month: HTML5 A control for entering a month and year, with no time zone.
- number: HTML5 A control for entering a number.
- password: A single-line text field whose value is obscured. Use the maxlength and minlength attributes to specify the maximum length of the value that can be entered.
- Note: Any forms involving sensitive information like passwords (e.g. login forms) should be served over HTTPS; Firefox now implements multiple mechanisms to warn against insecure login forms — see Insecure passwords. Other browsers are also implementing similar mechanisms.
- radio: A radio button, allowing a single value to be selected out of multiple choices.
- range: HTML5 A control for entering a number whose exact value is not important.
- reset: A button that resets the contents of the form to default values.
- search: HTML5 A single-line text field for entering search strings. Line-breaks are automatically removed from the input value.
- submit: A button that submits the form.
- tel: HTML5 A control for entering a telephone number.
- text: A single-line text field. Line-breaks are automatically removed from the input value.
- time: HTML5 A control for entering a time value with no time zone.
- url: HTML5 A field for entering a URL.
- week: HTML5 A control for entering a date consisting of a week-year number and a week number with no time zone.
Some input types are now obsolete:
- datetime: A control for entering a date and time (hour, minute, second, and fraction of a second) based on UTC time zone. This feature has been removed from WHATWG HTML.